 Y-T Reviewer
Y-T Reviewer
Overview
The Y-T Reviewer is a signal viewer that displays sample values against time. This viewer is optimized to display sample values from stored data, for small but also very large time ranges. The component offers a large number of properties to change its appearance and behavior. If a data source with stored data is connected to this viewer, the user is able to scroll through the signal data, and do in-place data analyses.Operator ports
Input S: Floating point valuesPaired User Interface Object
This operator is loaded simultaneously with a user interface object. The user interface object can be moved to another page, and would normally be displayed in the end-user application. The operator and this user interface object can never be separated. If you delete the operator, the user interface is deleted automatically as well. Note that you cannot delete the user interface, only the operator symbol!Properties
Find more information about changing properties here: linkSyncID
type: See descriptionIf this object should be synchronous with other review objects, then they should all have an ID, that you can think out yourself.
CenterCursorWidth
type: Real valueWidth of the center cursor that points to the current time. Default width is 1.
CenterCursorColor
type: Known color nameName of the color of the center cursor that points to the current time. The color comes from the Color Repository.
This property uses the Color Repository. For more information about the use of colors in a project, refer to link
CenterCursorPercent
type: Real valuePercentage of the signal view where the cursor is located (default 50%)
The Center Cursor is a colored vertical line, normally in the center of the signal review pane. It points to the sample that has the current time. This only has a meaning if more reviewers are synchronized (using their SyncID) and should point to the same sample. If you then move one reviewer, the others will also move to the sample the center cursor points to.
AllowScrolling
type: True or FalseSet to true if the end-user is allowed to scroll through the signals by dragging the mouse cursor to the left or right near the Center Cursor.
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
If you want to show data that fits in the viewer completely from the first sample on, then it doesn't make sense that the user can move the signal view to the left or the right. In that case you would set this property to False.
If scrolling is not allowed, the signals are always drawn starting from the first sample.
If scrolling is not allowed, the signals are always drawn starting from the first sample.
EnableSignalSelection
type: True or FalseSet to true to enable the user to select signals by dragging the mouse over the signals. This also enables the use of the SelectionStartValues and SelectionEndValues variable parameters.
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
Read more about signal selection and static data post processing in the details section of this document.
SelectionWindow
type: Real valueSpecifies a fixed width of a selection window in seconds. If set to -1, then a moving cursor is shown. If set to 0, then no cursor is shown and no signals are selected.
If a fixed selection window of greater than 0 seconds has been specified, then the user cannot freely select signals with a start and end point.
ShowMovingCursor
type: True or FalseSet to true to show a moving cursor with a flag containing sample values below the mouse pointer.
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
BackgroundColor
type: Known color nameThe color of the background.
This property uses the Color Repository. For more information about the use of colors in a project, refer to link
ForegroundColor
type: Known color nameThe color of the title, axes and other lines around the graph.
This property uses the Color Repository. For more information about the use of colors in a project, refer to link
GridColor
type: Known color nameThe color of the grid or markings.
This property uses the Color Repository. For more information about the use of colors in a project, refer to link
SelectionColor
type: Known color nameThe color for channel selections.
This property uses the Color Repository. For more information about the use of colors in a project, refer to link
BorderStyleOutside
type: See descriptionSelect a style for the outer border of the viewer.
BorderStyleInside
type: See descriptionSelect a style for the border of the panel where the viewer contents or graph is drawn.
Title
type: See descriptionThe title above the graph. You may use variables in the text.
Variables that are used as part of the viewer title are only updated if the viewer itself is updated, so you cannot for example display a clock as title.
One example of use is to display the name of the file that is currently viewed in the viewer. Your title then may look like this:
Viewing file $Design.File Replay.Caption$ (date: $Design.File Replay.FileDate$
One example of use is to display the name of the file that is currently viewed in the viewer. Your title then may look like this:
Viewing file $Design.File Replay.Caption$ (date: $Design.File Replay.FileDate$
Y_Label
type: See descriptionThe label along the Y-axis.
Y_LabelVisible
type: True or FalseSet to False to disable the label along the Y-axis
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
X_Label
type: See description [this value cannot be changed]The label along the X-axis.
X_LabelVisible
type: True or FalseSet to False to disable the label along the X-axis
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
FontTitle
type: Known text font nameThe text font of the title (select from the Font repository).
This property uses the Font Repository. For more information about the use of text fonts in a project, refer to link
FontMetaData
type: Known text font nameThe text font of all meta data, such as channel names (select from the Font repository).
This property uses the Font Repository. For more information about the use of text fonts in a project, refer to link
FontContents
type: Known text font nameThe text font of values and labels of the shown contents or graph (select from the Font repository).
This property uses the Font Repository. For more information about the use of text fonts in a project, refer to link
SingleBaseline
type: True or FalseSet this value to 'true' if you want all the signals to be drawn around one baseline.
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
ExtraRoomTopBottom
type: True or FalseIf true, a full baseline distance is added above the first channel and below the last; if false only half a baseline distance is added. If only one channel is visible, this setting may influence your Range/Offset settings.
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
Per default, the distance between a signal baseline and the top or bottom of the view pane, is equal to the distance between two baselines. If however only one baseline with signals is displayed in the viewer, the extra room above or below a baseline makes it very difficult to set the range or offset of the signals. For example, if you require a single baseline to be on the bottom of the view pane, you would set this property to False.
AllowChannelSelect
type: True or FalseIf true, the user is able to select channels by clicking one or more channel names.
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
AllowZooming
type: True or FalseSet to true if the end-user is allowed to change the time range from within the viewer, by scrolling the scroll wheel of the mouse.
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
NumberFormat
type: See descriptionDetermines how values are displayed in the viewer. Examples: ',2' (decimal comma), '.3' (decimal dot), ';1' (decimal comma or dot). This only regulates sample values, not time labels.
For more information about Number Formats, please refer to link.
ClockTime
type: True or FalseDetermines if times are displayed as a continuous time (set to false), or as clock time (set to true). Clock time makes the time always be between 12 or 24 hours (depending on your culture).
Select one of those presets:
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
True or False
True may also be read like 'yes' and false like 'no'
In Clock Time mode, the viewer assumes the sample time to be a time in one day. The sample with t=0 is then considered to occur at midnight.
After 24 hours worth of samples, the time will change from 24:00:00 to 0:00:00 (or 12:00:00 AM, or similar).
The time that is displayed is formatted according to the cultural settings of your operating system.
After 24 hours worth of samples, the time will change from 24:00:00 to 0:00:00 (or 12:00:00 AM, or similar).
The time that is displayed is formatted according to the cultural settings of your operating system.
BackgroundImage
type: Known image nameThe name of the background image. The image name can be selected from the Image Repository (press the small button).
This property uses the Image Repository. For more information about the use of images in a project, refer to link
Caption
type: Word or phraseThe name of the object in the project. This name must not contain '.' or '$' characters.
Every object has the Caption property. This property is very important, because it is the name by which Polybench recognizes this object.
It is allowed to give multiple objects the same name, as long as the objects are of the same type. In that case, a reference to this caption includes all the objects with the same caption.
In Polybench, every object can be addressed by an Address specifier, which starts with the dollar sign, for example: $My Page.My Object. 'My Page' would be the Caption of a page, and 'My Object' the Caption of an object on that page.
It is allowed to give multiple objects the same name, as long as the objects are of the same type. In that case, a reference to this caption includes all the objects with the same caption.
In Polybench, every object can be addressed by an Address specifier, which starts with the dollar sign, for example: $My Page.My Object. 'My Page' would be the Caption of a page, and 'My Object' the Caption of an object on that page.
Documentation
type: See descriptionOptional documentation of this object.
It is good practice to write in short notes why you have used this object, and why its properties are set the way they are set. If this object is an operator, the Documentation text is displayed below the operator symbol.
Extra dialog to change properties of this object: Layout
Variable Parameters
Find more information about Variable Parameters here: linkPostProcInformation
type: Parameter list (see link)List with information that can be used by other post processing components.
TimeSyncOffset
type: See descriptionThe time offset of the data cursor for this viewer. If you link multiple data review components together (using a SyncID), then this viewer will show a time offset. The time is expressed in hour:minute:second, or in seconds.
CursorTime
type: See descriptionThe time at the cursor in the viewer. The time is displayed as a time value.
CursorTimeSeconds
type: See descriptionThe time at the cursor in the viewer. The time is displayed in seconds and has a maximal resolution of 0.01 millisecond.
SelectionWindow
type: See descriptionSpecifies a fixed width of a selection window in seconds. If set to -1, then a moving cursor is shown. If set to 0, then no cursor is shown and no signals are selected.
SelectionTimeSpanSeconds
type: See descriptionThe time span of the current selection. The time is displayed in seconds and has a maximal resolution of 0.01 millisecond.
SelectionEndValues
type: Parameter list (see link)List of values of every channel on the end of the signal selection in the reviewer. All channels are returned; not only the ones that are visible in the viewer.
SelectionStartValues
type: Parameter list (see link)List of values of every channel on the start of the signal selection in the reviewer. All channels are returned; not only the ones that are visible in the viewer.
CursorValues
type: Parameter list (see link)List of values of every channel on the cursor in the reviewer. All channels are returned; not only the ones that are visible in the viewer.
ImageName
type: See descriptionThe name of the background image, which is an image in the Image Repository
TimeLabelOffset
type: See descriptionThe time offset of the time labels in the viewer. Setting this value will change the time that is displayed for the current signals. The time is expressed in hour:minute:second, or in seconds.
ClockTime
type: See descriptionDetermines if times are displayed as a continuous time (set to 1), or as clock time (set to 0). Clock time makes the time always be between 12 or 24 hours (depending on your culture).
In Clock Time mode, the viewer assumes the sample time to be a time in one day. The sample with t=0 is then considered to occur at midnight.
After 24 hours worth of samples, the time will change from 24:00:00 to 0:00:00 (or 12:00:00 AM, or similar).
The time that is displayed is formatted according to the cultural settings of your operating system.
After 24 hours worth of samples, the time will change from 24:00:00 to 0:00:00 (or 12:00:00 AM, or similar).
The time that is displayed is formatted according to the cultural settings of your operating system.
Functions
Find more information about Functions here: linkAutoScale
Changes the range and offset of all (or selected) channels in a way, that all signals in the current view are entirely visible. There must be a preparation operator before the viewer operator that set the ranges and offsets, e.g. the Prepare Ranges and Offsets (link).AutoRange
Changes the range of all (or selected) channels in a way, that the signals in the current view are entirely visible, without changing the offset. There must be a preparation operator before the viewer operator that set the ranges and offsets, e.g. the Prepare Ranges and Offsets (link).AutoOffset
Changes the offset of all (or selected) channels in a way, that the signals in the current view are evenly spread in the view, without changing the range. There must be a preparation operator before the viewer operator that set the ranges and offsets, e.g. the Prepare Ranges and Offsets (link).
Details
Stored data viewer
Polybench distinguishes between real-time data and stored data. Real-time data is data that flows (possibly in real-time) through all signal processing operators. Stored data is data in a data file that can be viewed ad hoc.If you want to display real-time signal data, you need the Y-T Viewer (link), but to view and scroll through stored data, you need the Y-T Reviewer. Note that the Y-T Reviewer cannot display real-time data, so if you connect a real-time signal source to its input, no data will appear.
Connecting to a stored data source
This viewer is always directly connected to a storage-type operator (for example the File Replay link or the Storage link). The only operators that may be placed between the storage and the reviewer are the Viewer Preparation operators (link), such as the Prepare Ranges and Offsets (link). Any other operator will break the stored data connection, so that no signals are visible in the viewer.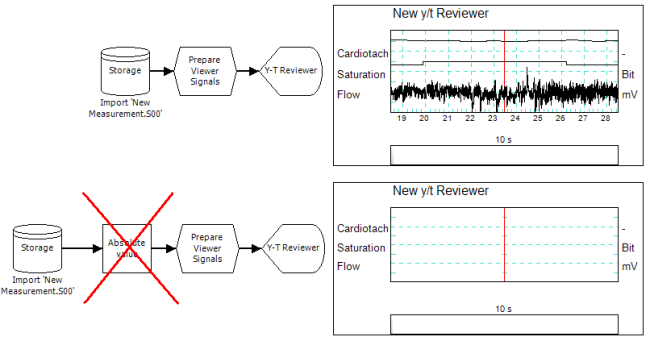
Scrolling through the signals
The Y-T Reviewer offers two ways to scroll through a long signal file; either by shifting the scrollbar below the signals, or by dragging your mouse in the signal pane. The dragging works like this:- put your mouse pointer near the Center Cursor. The Center Cursor is a vertical line that by default is drawn in the middle of the signal view (you may set its width, color and position in the properties).
- hold the mouse button down
- now slowly drag to the right and observe how the signals scroll to the left - and vise versa.
- the further you drag the mouse from the Center Cursor, the quicker the signals scroll
This way of scrolling was selected to be the most practical one for long signal files. It allows the user to look through large ranges of signals with only small gestures.
If your mouse pointer hovers over the signal pane, you may also use the scroll wheel of your mouse to zoom the time range in or out.
Signal selection and static data processing
If the EnableSignalSelection property is set to true, the user can drag his mouse in the signal view and so select signals. All channels are selected at once, but a label shows the value and time of the channel the mouse is currently over.If the user is ready selecting signals, the selection is retained; also if the time base is changed or any signal properties are changed. To remove the selection, click somewhere in the signal view.
In the variable parameters of the Y-T Reviewer, the signal values of the start and end of the selection are made available. You may use these values to do simple calculations or make value displays.
The selection in one Y-T Reviewer can be communicated to a parallel Y-T Reviewer, so that the same selection is shown in the other viewer. To be able to do this, both Y-T Reviewers need to be connected to the same Prepare Viewer Signals operator (link). It is allowed to place multiple other preparation operators in between, but in the end both viewers should come together in this Prepare Viewer Signals.
User Interface Object on Printable Pages
The user interface of this component will be printed on a report, if it is put on a Printable Page (see link).Behaviour in relation to the data cursor in reviewed data
This object reacts on a change of the central Data Cursor of a group of synchronized objects. This means that if this object has the same SyncID as the object that changes the Data Cursor, then this object will change its state accordingly. For more information see also: link.Examples
Example: AutoScale, Auto Range and AutoOffset Demo
This demo shows the difference between the AutoScale, AutoRange and AutoOffset functions of Y-T Viewers. Those three functions are related, but either of them will make sense for specific signal views, with specific time ranges, and user requirements.For example, viewer 1 at 35 sec time range will profit most from the AutoScale. Viewer 3 at 5 sec time range could very well use AutoOffset, to let the view move along with the signal. Viewer 2 at 5 sec time range changes its amplitute and could profit from AutoRange. Which of the functions is the right one, also strongly depends on user requirements.
Just try out the possibilities in this demo!
Examples\DF0306026_001_AutoScale_AutoRange_AutoOffset_Demo.xmc
Example: Reviewer cursor change by actions Demo
Demonstrates the CursorTimeSeconds variable. In a Variable Viewer, the current value is displayed. There are also two Action Buttons that change the time value and add or subtract 20 seconds of the time.Examples\DF0306026_002_Reviewer_cursor_change_by_actions_Demo.xmc
